Try using these words to better communicate with clients, coworkers, or a developer. They will think you really know your sh*t…because you do. 😎
1. Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are little sub-navigation links that are typically near the top of the page. Most commonly used in online stores to show which subcategory you’re currently in. Just like leaving a trail of breadcrumbs!
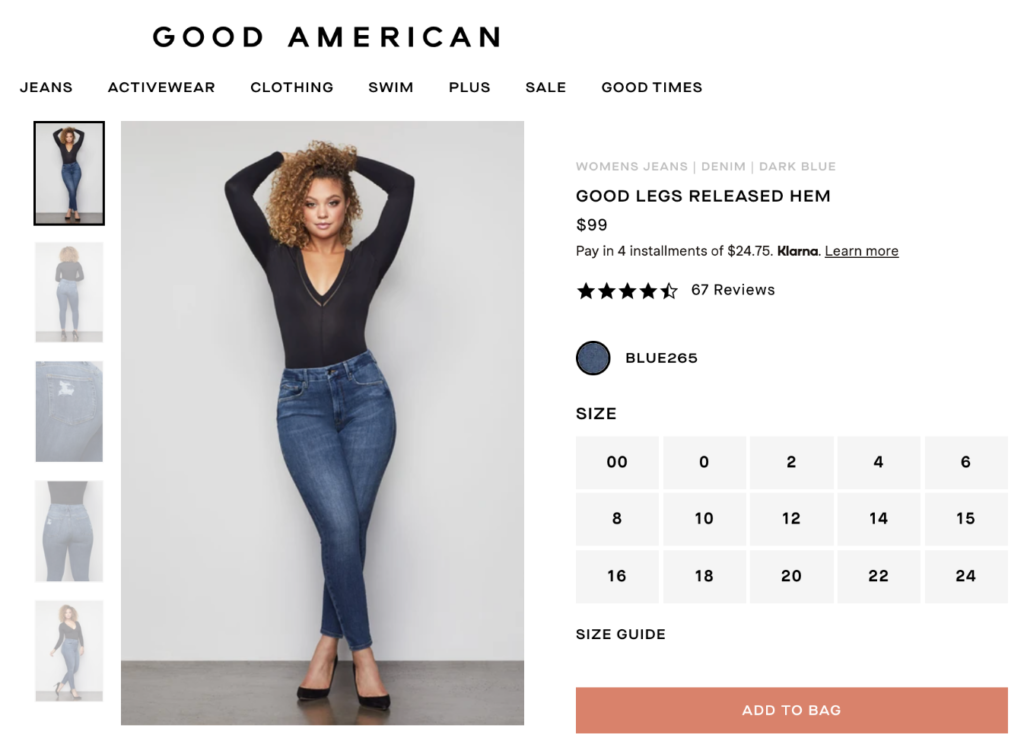
2. Hero Section
The hero section is the very first portion of a website that you see. It consists of THE most important information on the whole site—your main heading and call-to-actions. This is the section where you show people who you are and what you do at a quick glance; hence the name, “hero” section.
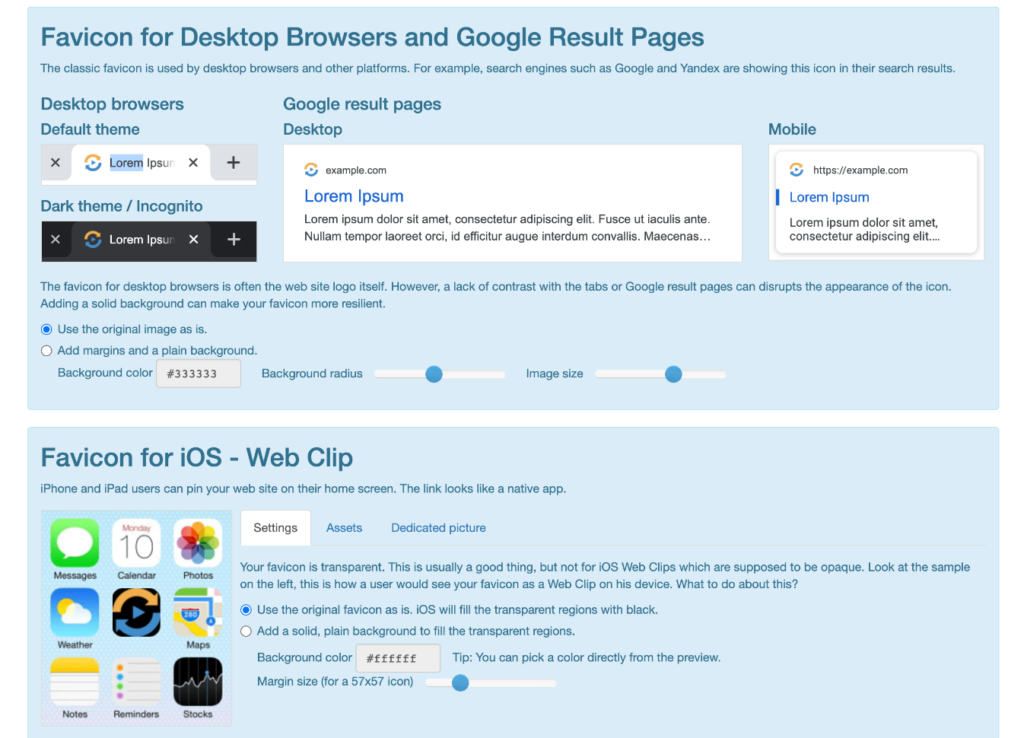
3. Favicon
Your favicon is the little tiny icon that shows in the browser tab next to the URL. It’s also the icon that shows on Google’s search result pages, as well as the bookmark image on a mobile device.
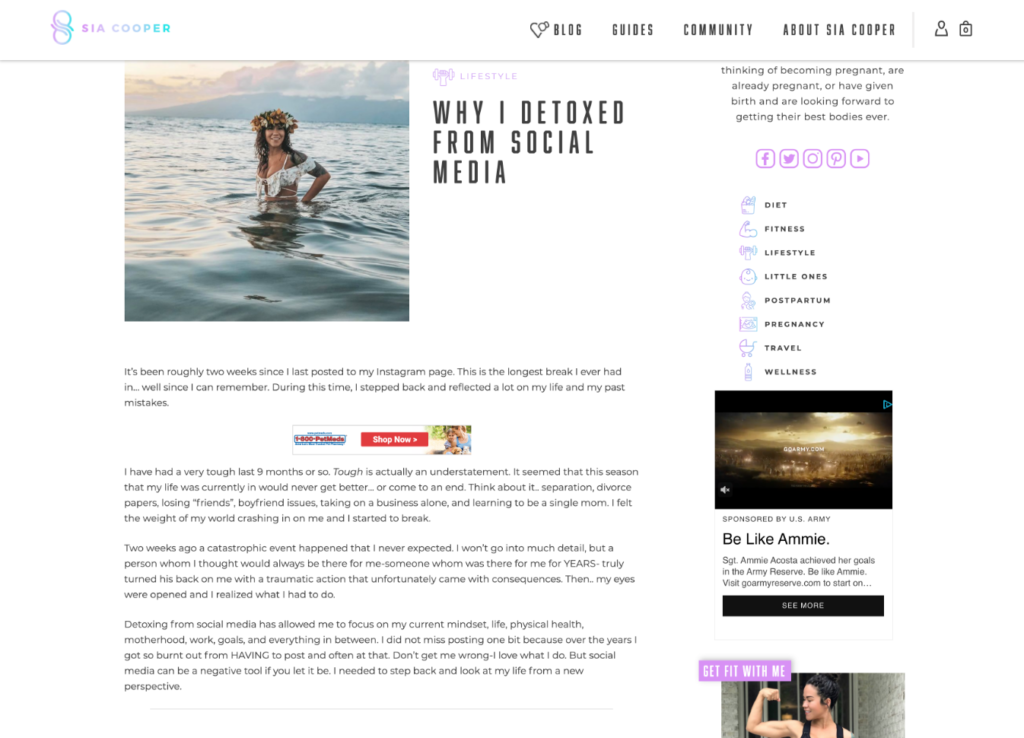
4. Sticky
The term “sticky” refers to an element on a page that stays “stuck”, or anchored, while everything else scrolls. It’s most commonly used to describe a sticky menu—which stays at the top of the page while you scroll.
5. Ghost Button
A ghost button isn’t as spooky as it sounds. It only means that the button has a transparent background. They are typically used to create a minimalist look and to not draw as much attention as a primary button.
In the example below—a video plays in the background, so it helped to keep the focus on the video.
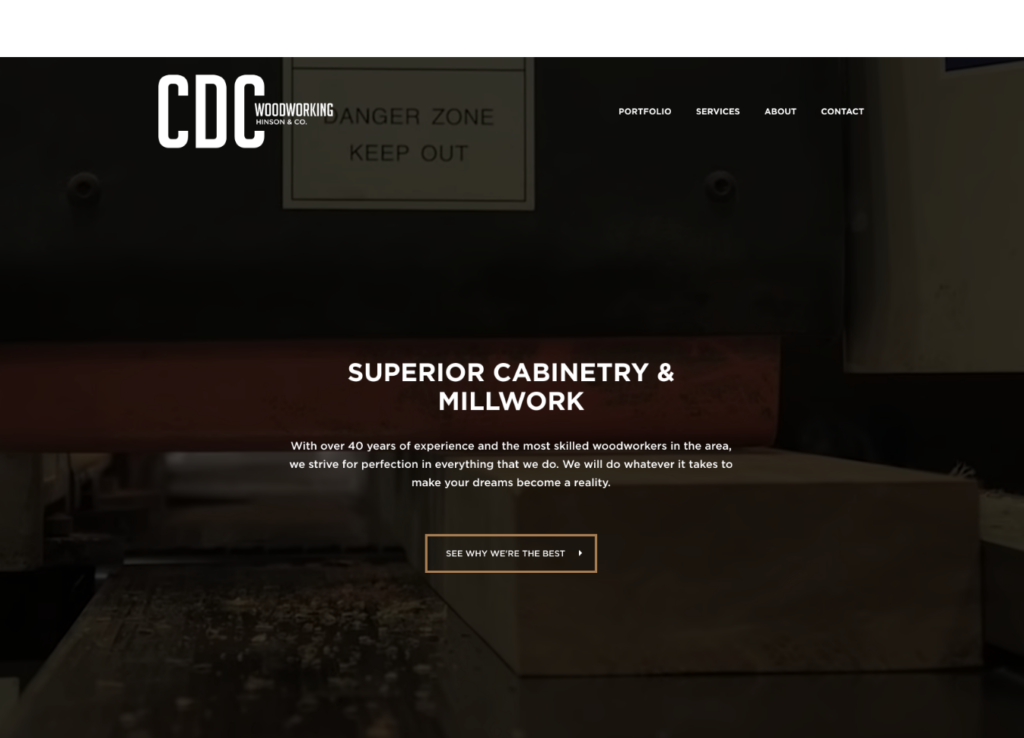
6. Anchor Link
In a nutshell, an “anchor” links to another section on the same page. These are most often used on one-page websites, which have a full navigation menu, but only one page of content. Clicking on the menu scrolls you down to a different section on the page.
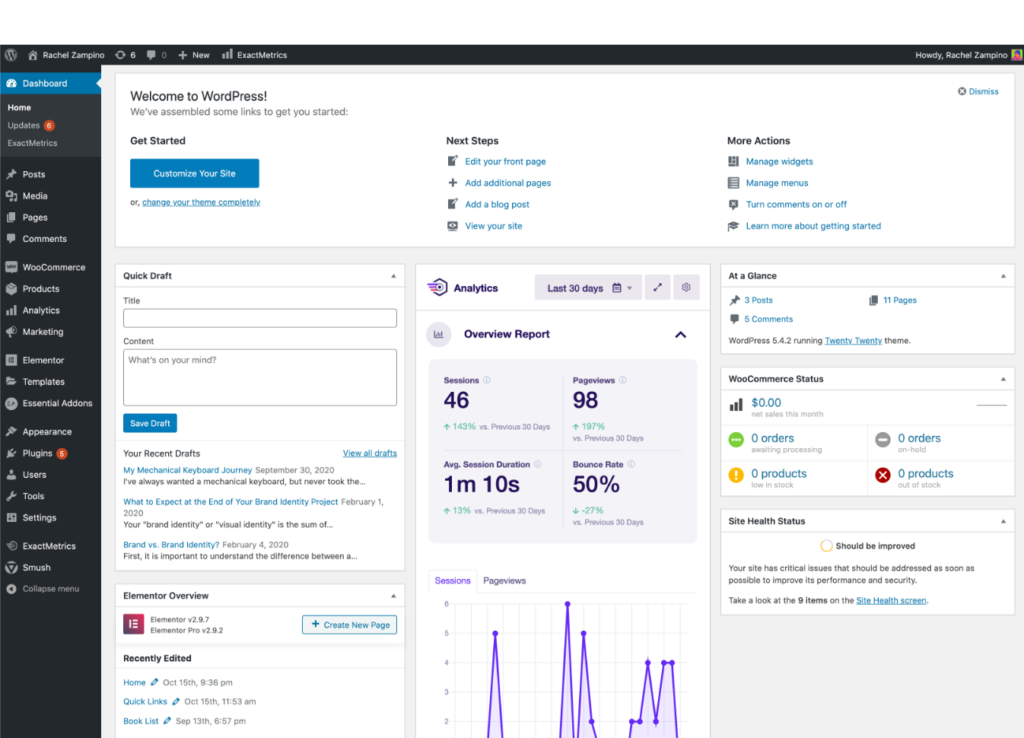
7. CMS
A content management system, or CMS, is a software that you can use to manage your website content. Instead of tinkering with code, they offer a user interface to interact with to make changes to your website.
WordPress, the most popular CMS, is pictured below.
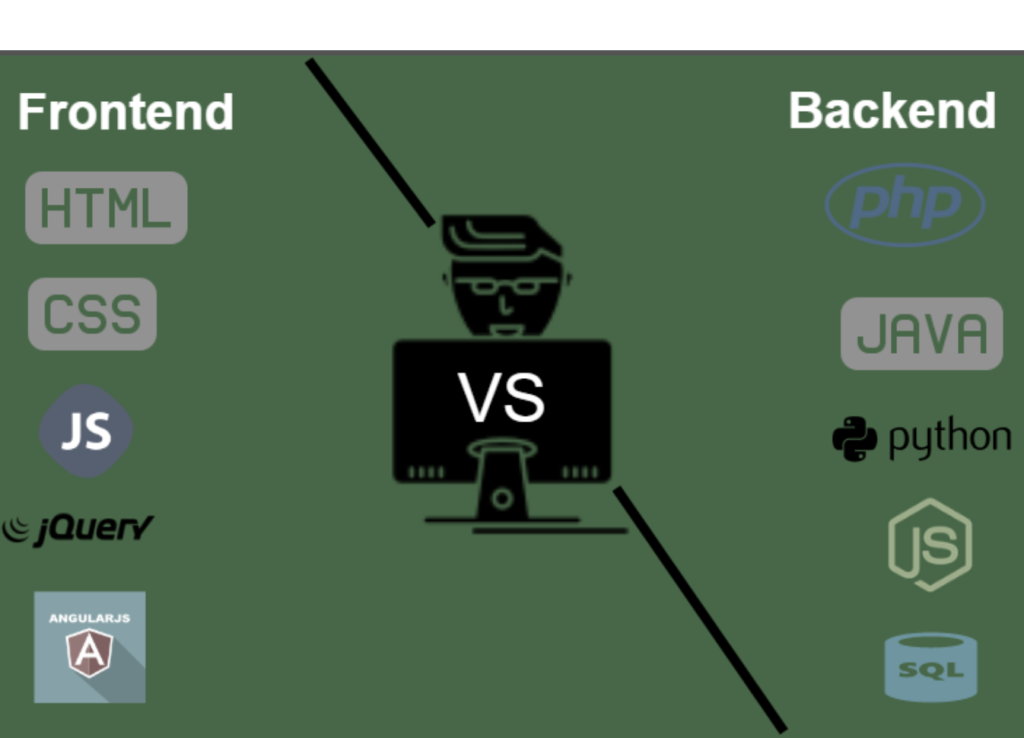
8. Front-end vs. Back-end
My simplest explanation is…
Front-end = form, how it looks
Back-end = function, how it works
Here’s a super scary graphic of front-end vs. back-end programming languages…
Ta-dah! Now go and impress the World Wide Web with all of your new lingo!
- Updated on
Get biz & website tips in your inbox 💌
Sign up for the email list for free tutorials, cool tools, and DIY tips!
Jump to a section:
Save or share this post
Leave a comment

Rachel Zampino
Website Wizard
Hi! I’m Rachel Zampino, freelance WordPress developer and digital designer. Here to share all of my business and website tips with you.
If you enjoyed this post, consider buying me a coffee to show your support — or hire me to build you a website that you’ll be proud to show off!

